FRENIC-MEGA (G2)
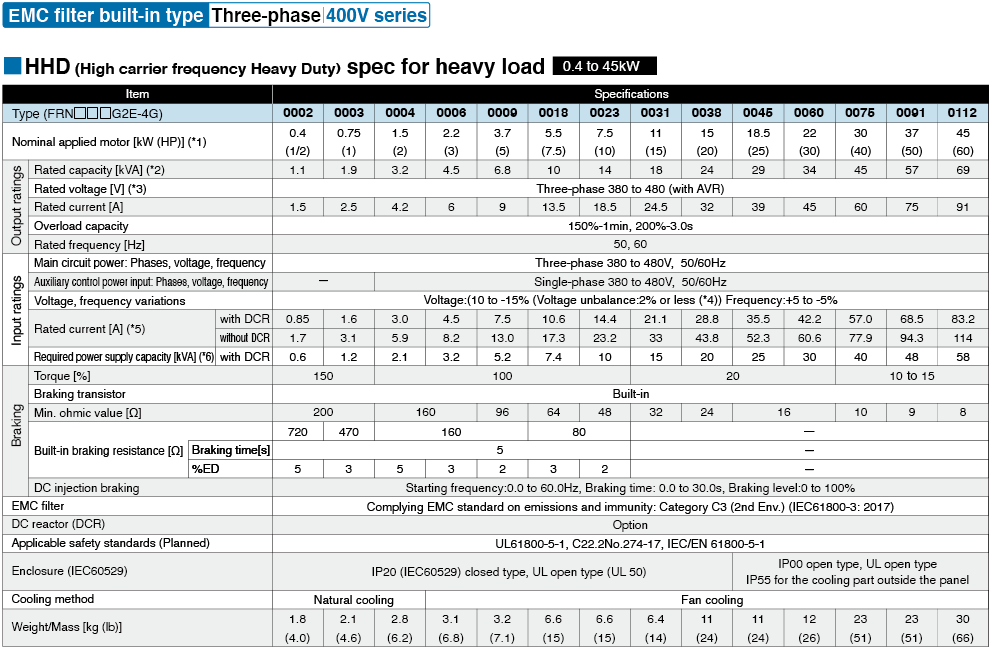
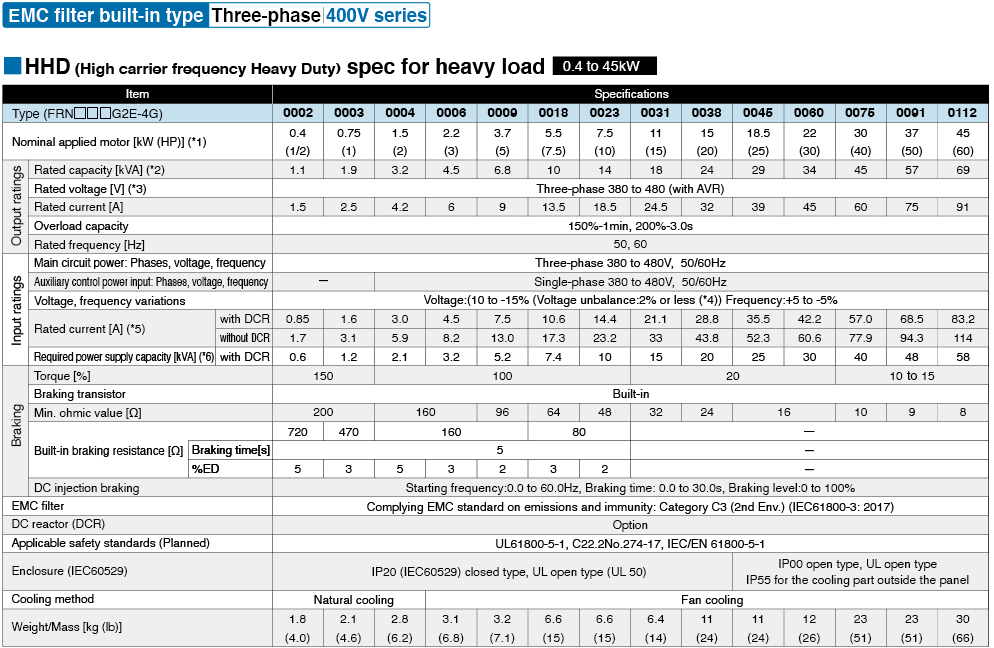
Specifications | EMC filter bulit-in type
-
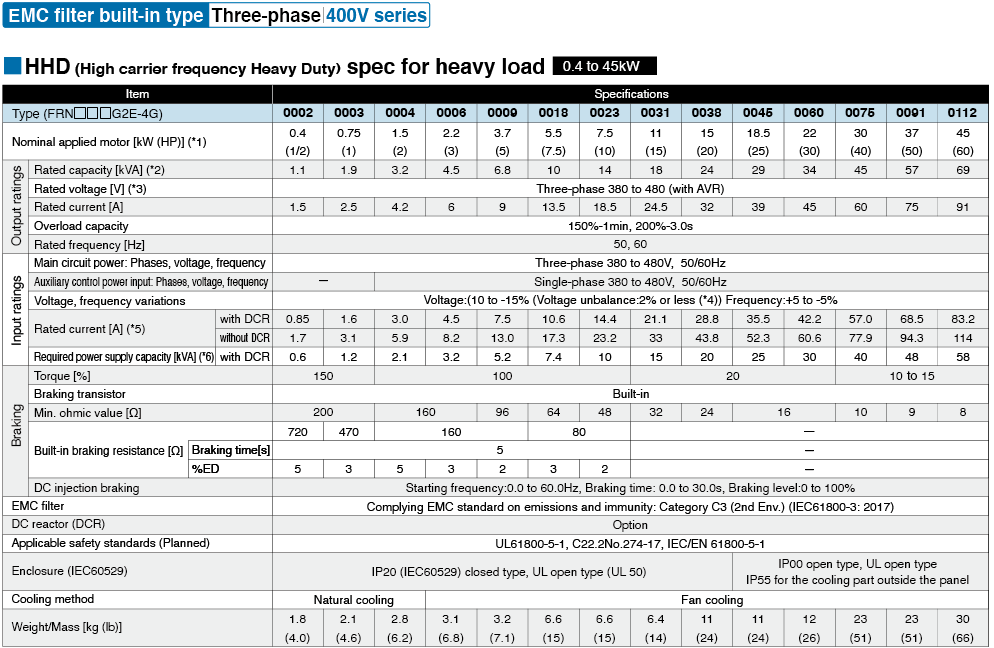
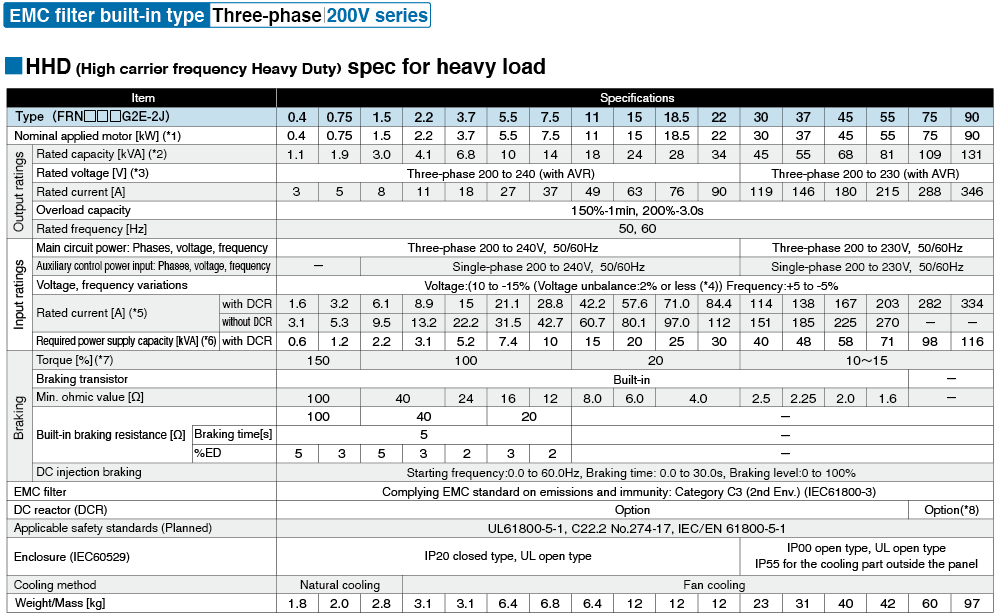
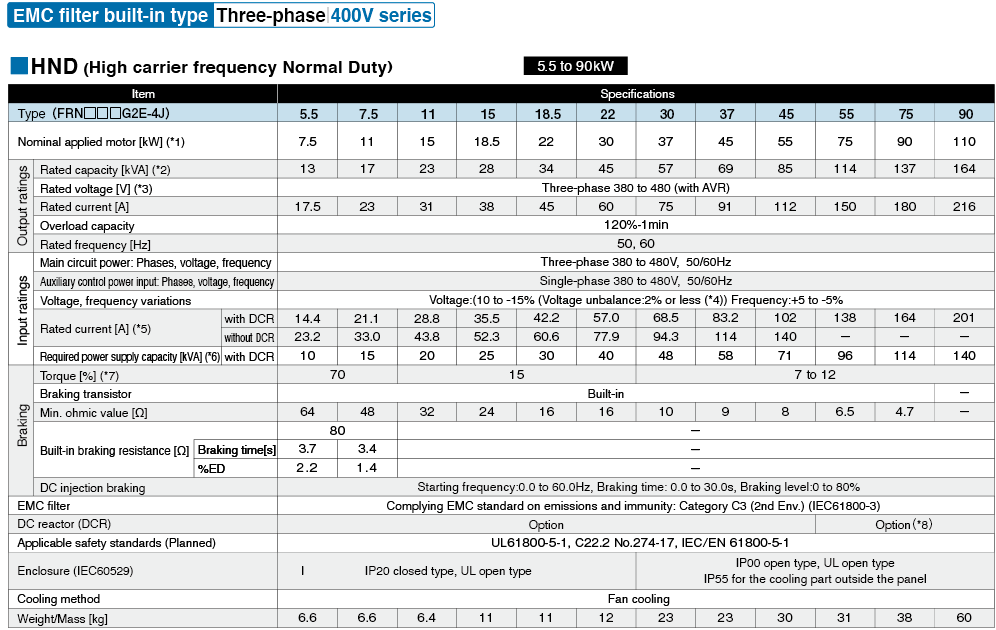
*1
-
Fuji's 4-pole standard motor When selecting an inverter, in addition to considering the kWs of the inverter, make sure that the output current rating is larger than the motor current rating.
-
*2
-
Rated capacity is calculated by assuming the rated output voltage as 220 V for 200 V series and 440 V for 400 V series.
-
*3
-
Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
-
*4
-
Voltage unbalance(%) =Max. voltage (V) - Min. voltage (V) / Three-phase average voltage (V) ×67 (IEC 61800-3)
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an optional AC reactor (ACR).
-
*5
-
These values are calculated on assumption that the inverter is connected to a power supply with a capacity of 500 kVA (or 10 times the inverter capacity when the inverter capacity exceeds 50 kVA) and %X is 5%.
-
*6
-
Required when a DC reactor (DCR) is used.
-
*7
-
When using a motor with a rating of 75 kW or more, be sure to use a DC reactor (option).
-
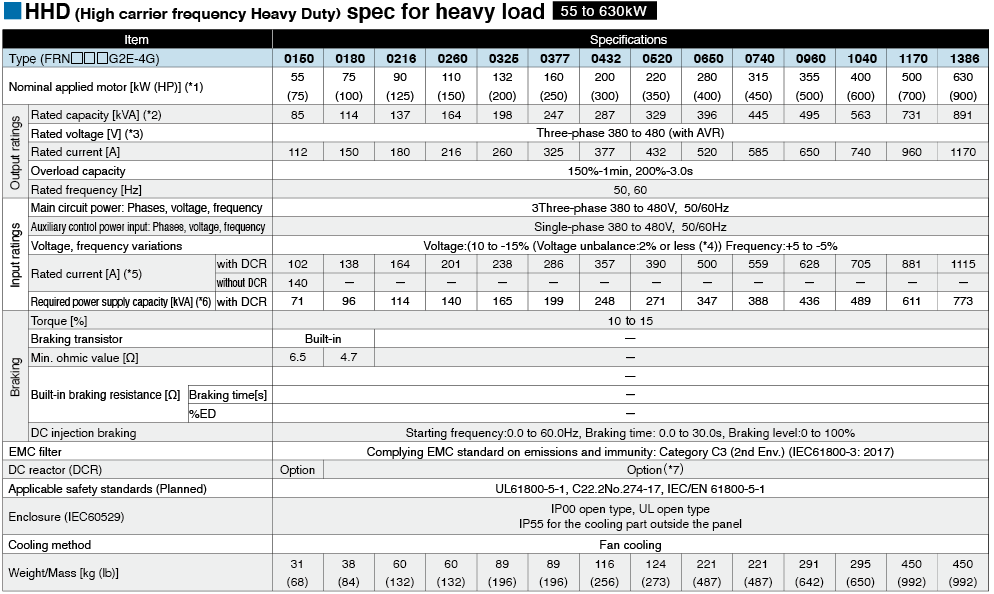
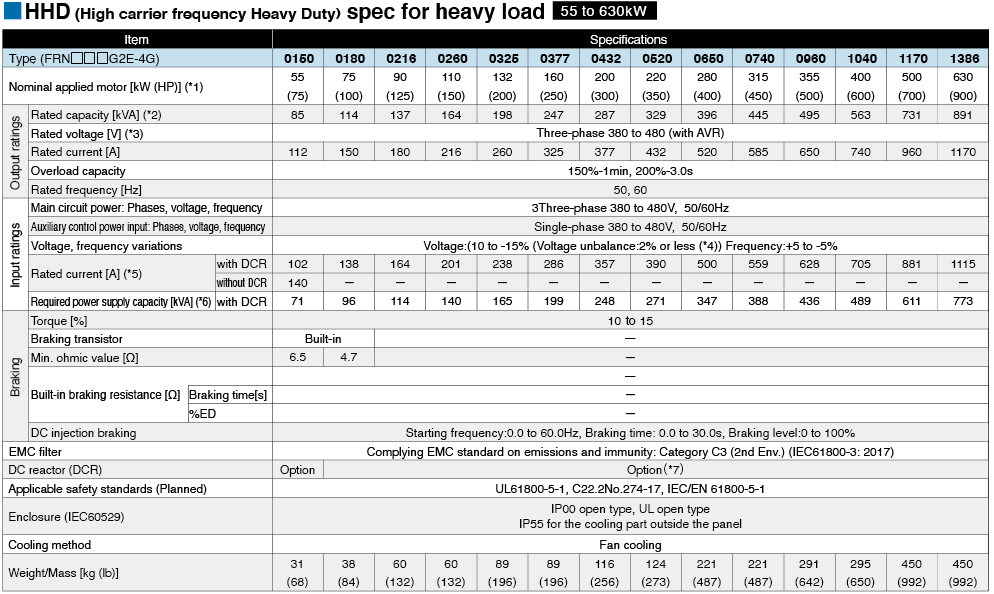
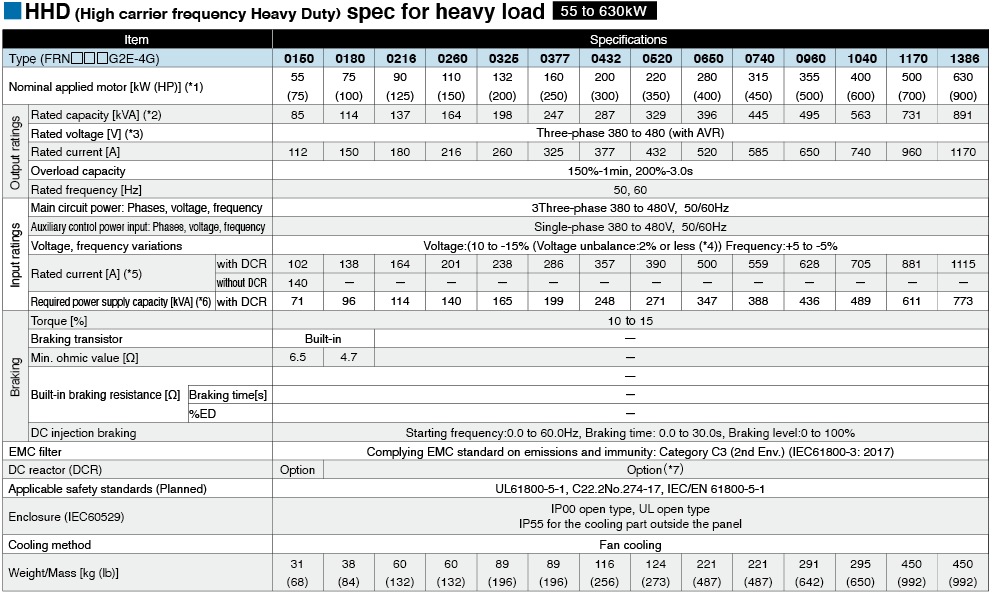
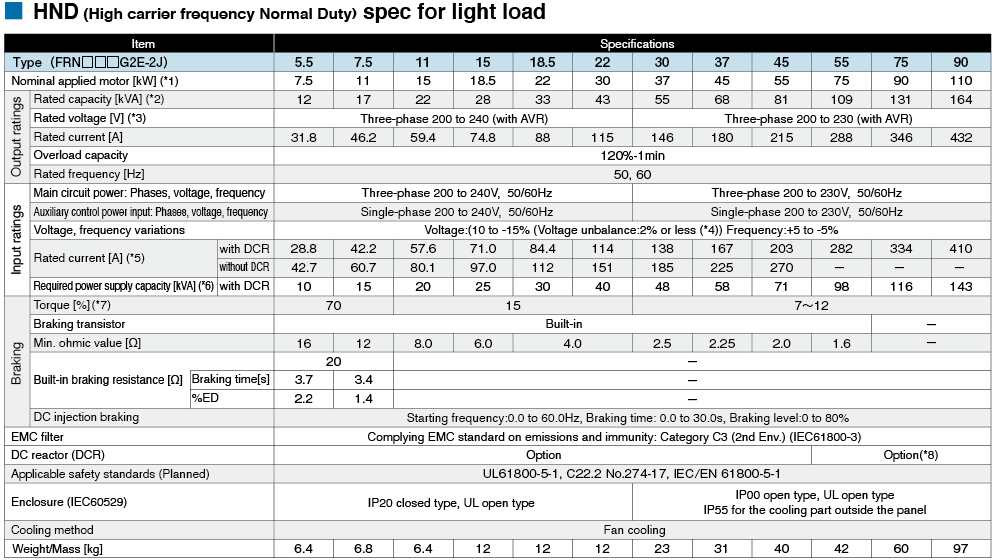
*1
-
Fuji's 4-pole standard motor When selecting an inverter, in addition to considering the kWs of the inverter, make sure that the output current rating is larger than the motor current rating.
-
*2
-
Rated capacity is calculated by assuming the rated output voltage as 220 V for 200 V series and 440 V for 400 V series.
-
*3
-
Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
-
*4
-
Voltage unbalance(%) =Max. voltage (V) - Min. voltage (V) / Three-phase average voltage (V) ×67 (IEC 61800-3)
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an optional AC reactor (ACR).
-
*5
-
These values are calculated on assumption that the inverter is connected to a power supply with a capacity of 500 kVA (or 10 times the inverter capacity when the inverter capacity exceeds 50 kVA) and %X is 5%.
-
*6
-
Required when a DC reactor (DCR) is used.
-
*7
-
When using a motor with a rating of 75 kW or more, be sure to use a DC reactor (option).
-
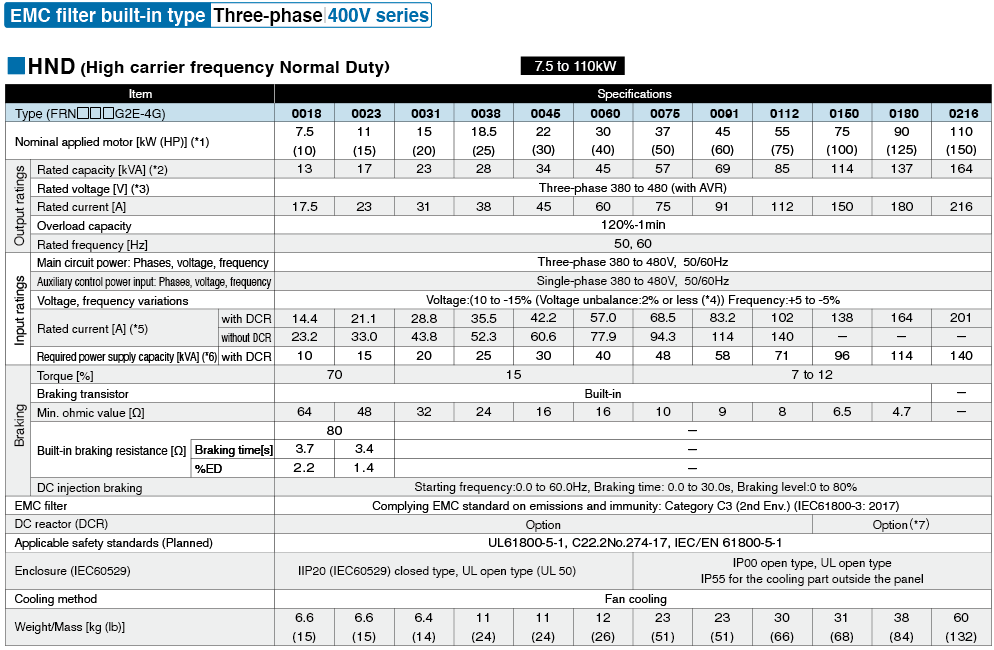
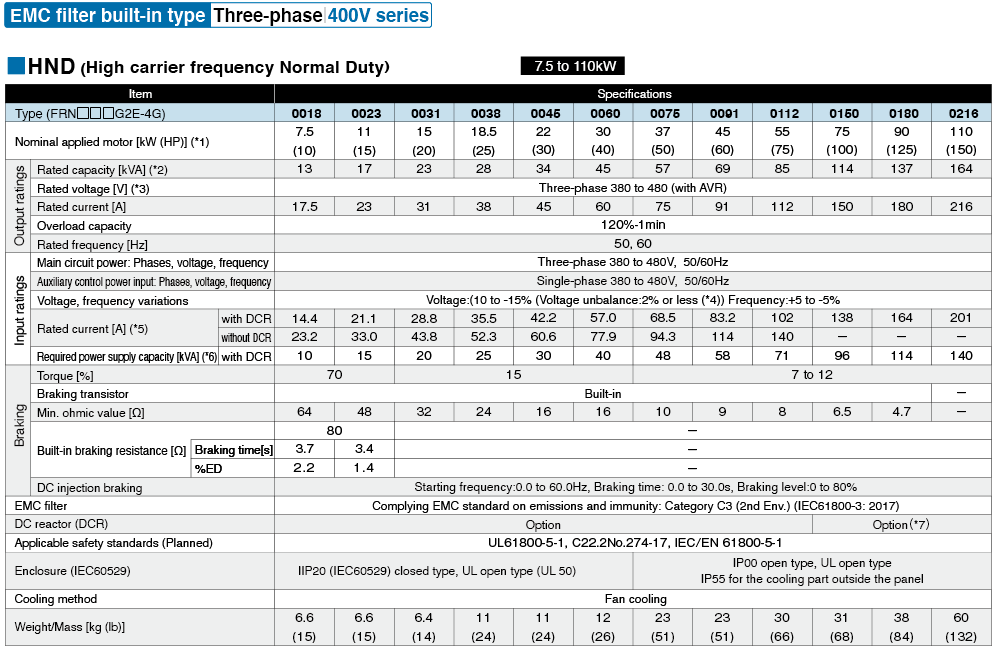
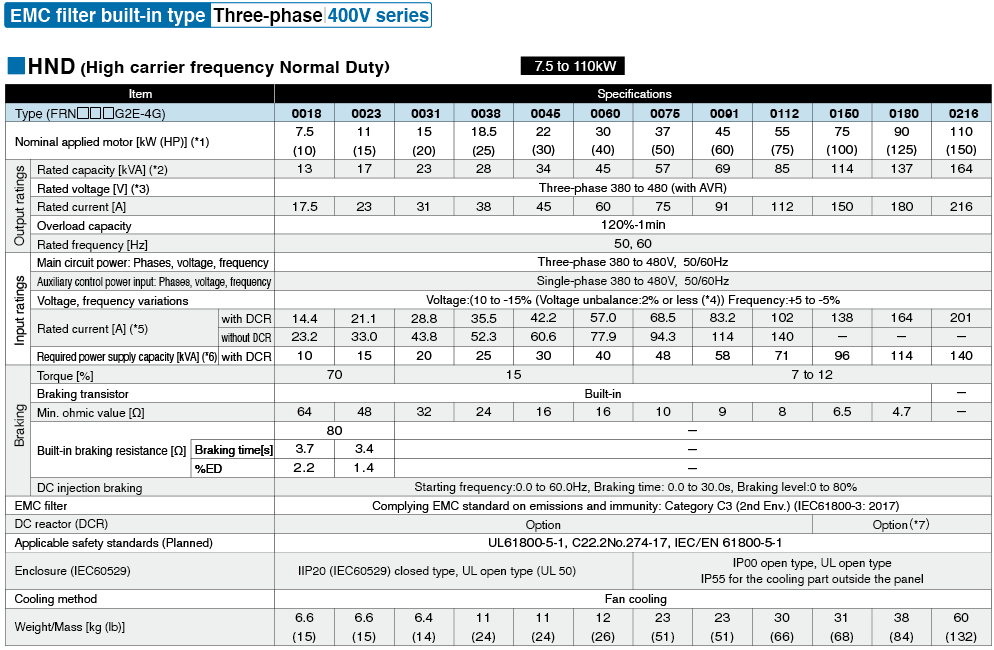
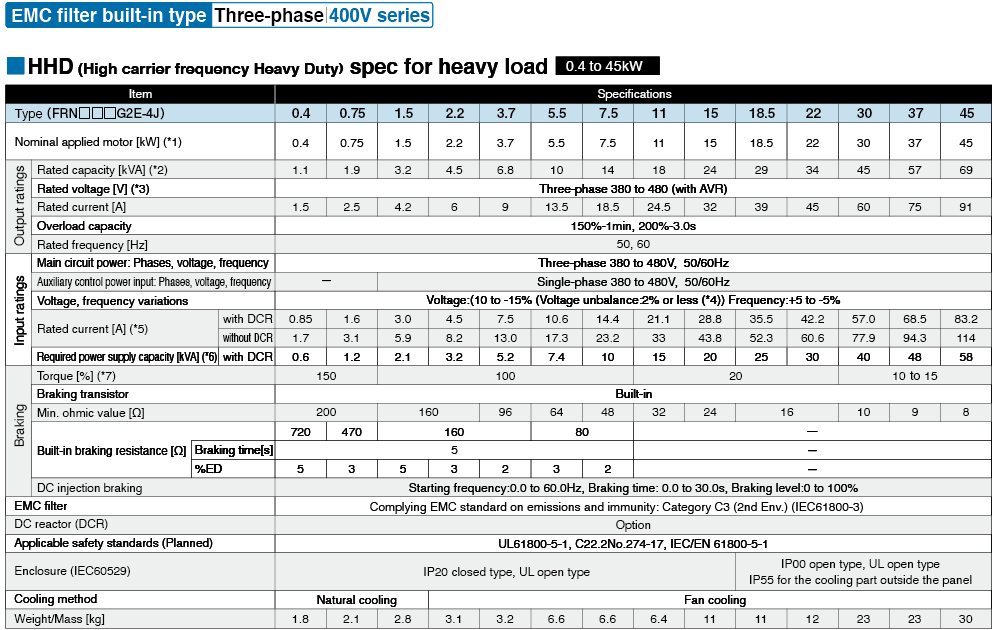
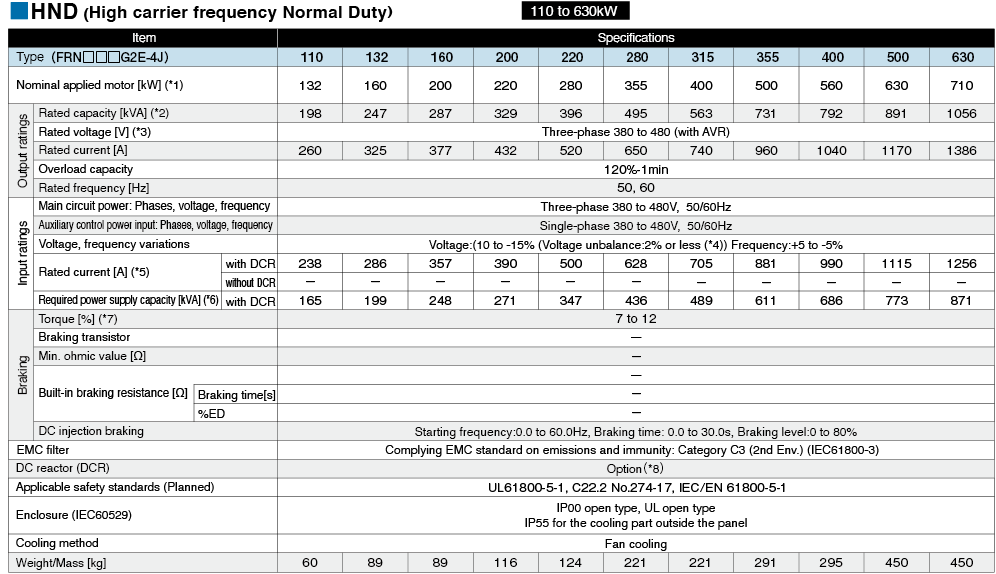
*1
-
Fuji's 4-pole standard motor When selecting an inverter, in addition to considering the kWs of the inverter, make sure that the output current rating is larger than the motor current rating.
-
*2
-
Rated capacity is calculated by assuming the rated output voltage as 220 V for 200 V series and 440 V for 400 V series.
-
*3
-
Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
-
*4
-
Voltage unbalance(%) =Max. voltage (V) - Min. voltage (V) / Three-phase average voltage (V) ×67 (IEC 61800-3)
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an optional AC reactor (ACR).
-
*5
-
These values are calculated on assumption that the inverter is connected to a power supply with a capacity of 500 kVA (or 10 times the inverter capacity when the inverter capacity exceeds 50 kVA) and %X is 5%.
-
*6
-
Required when a DC reactor (DCR) is used.
-
*7
-
When using a motor with a rating of 75 kW or more, be sure to use a DC reactor (option).
-
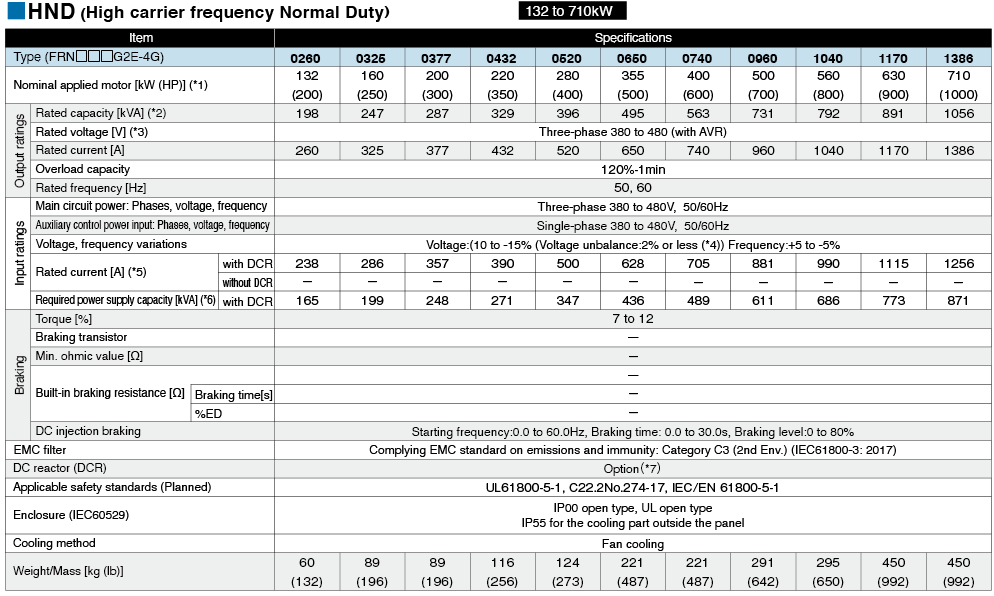
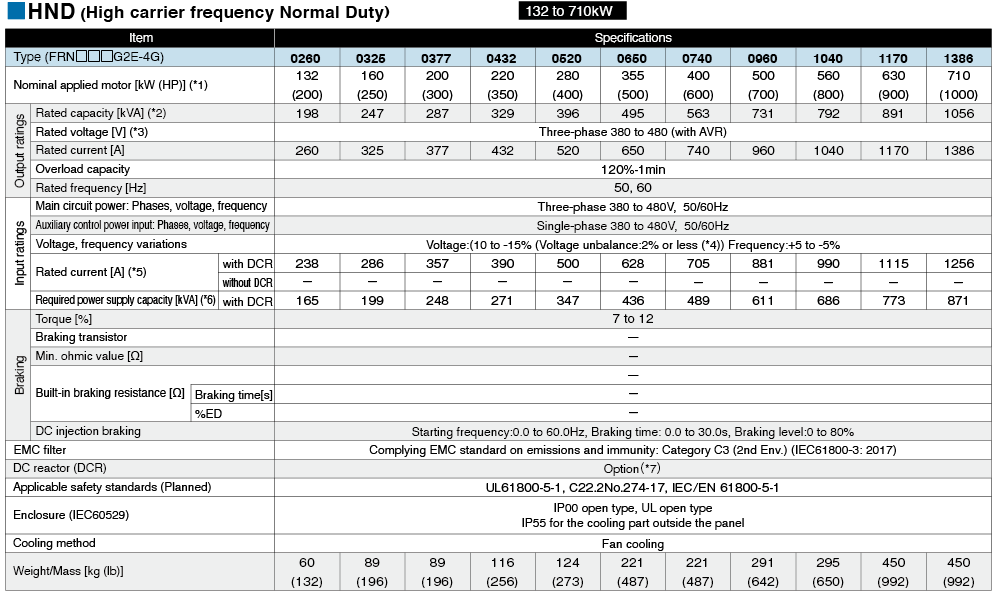
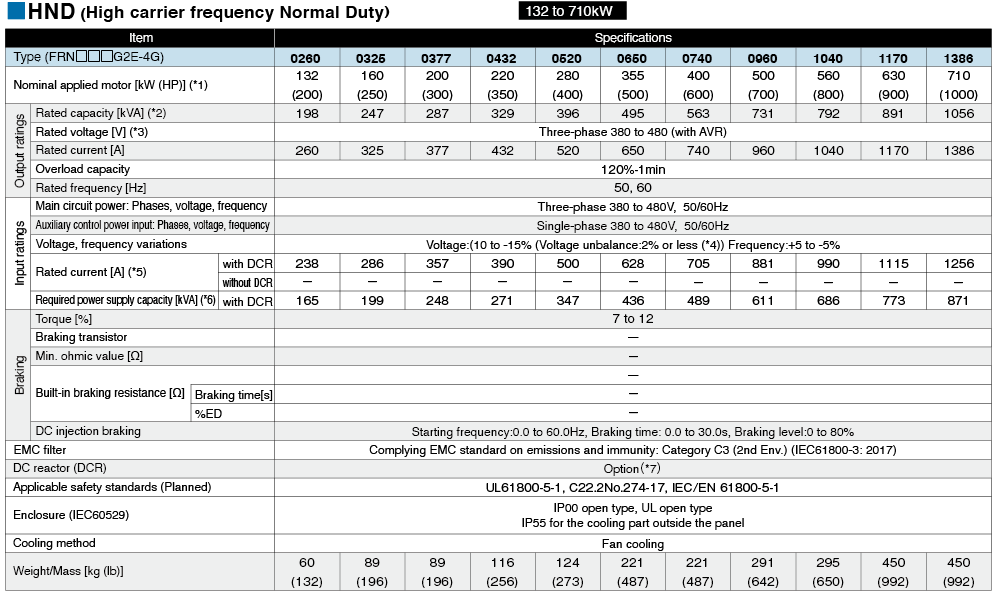
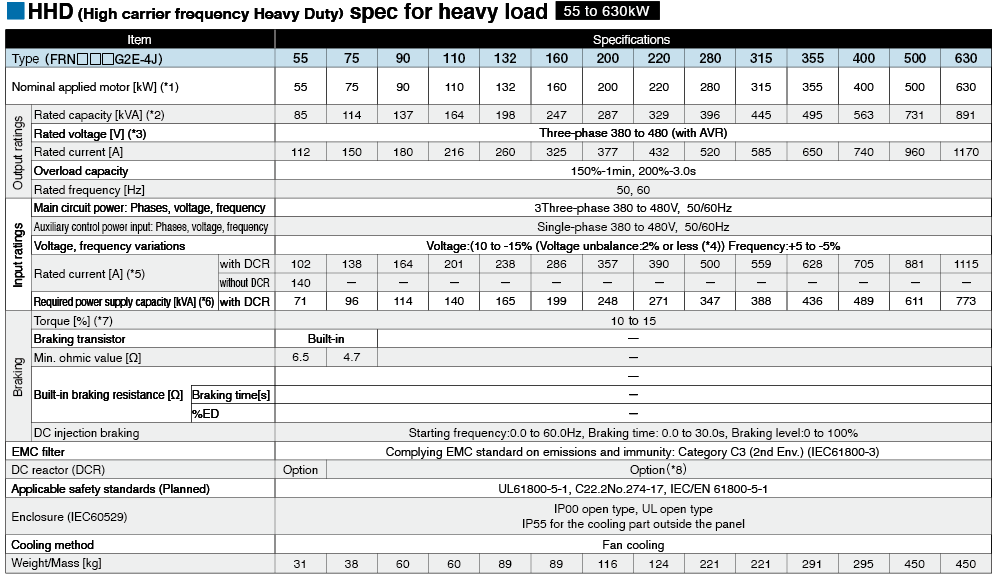
*1
-
Fuji's 4-pole standard motor When selecting an inverter, in addition to considering the kWs of the inverter, make sure that the output current rating is larger than the motor current rating.
-
*2
-
Rated capacity is calculated by assuming the rated output voltage as 220 V for 200 V series and 440 V for 400 V series.
-
*3
-
Output voltage cannot exceed the power supply voltage.
-
*4
-
Voltage unbalance(%) =Max. voltage (V) - Min. voltage (V) / Three-phase average voltage (V) ×67 (IEC 61800-3)
If this value is 2 to 3%, use an optional AC reactor (ACR).
-
*5
-
These values are calculated on assumption that the inverter is connected to a power supply with a capacity of 500 kVA (or 10 times the inverter capacity when the inverter capacity exceeds 50 kVA) and %X is 5%.
-
*6
-
Required when a DC reactor (DCR) is used.
-
*7
-
This is the average braking torque value for the motor on its own. (This will vary based on the motor efficiency.)
-
*8
-
When using a motor with a rating of 75 kW or more, be sure to use a DC reactor (option).














