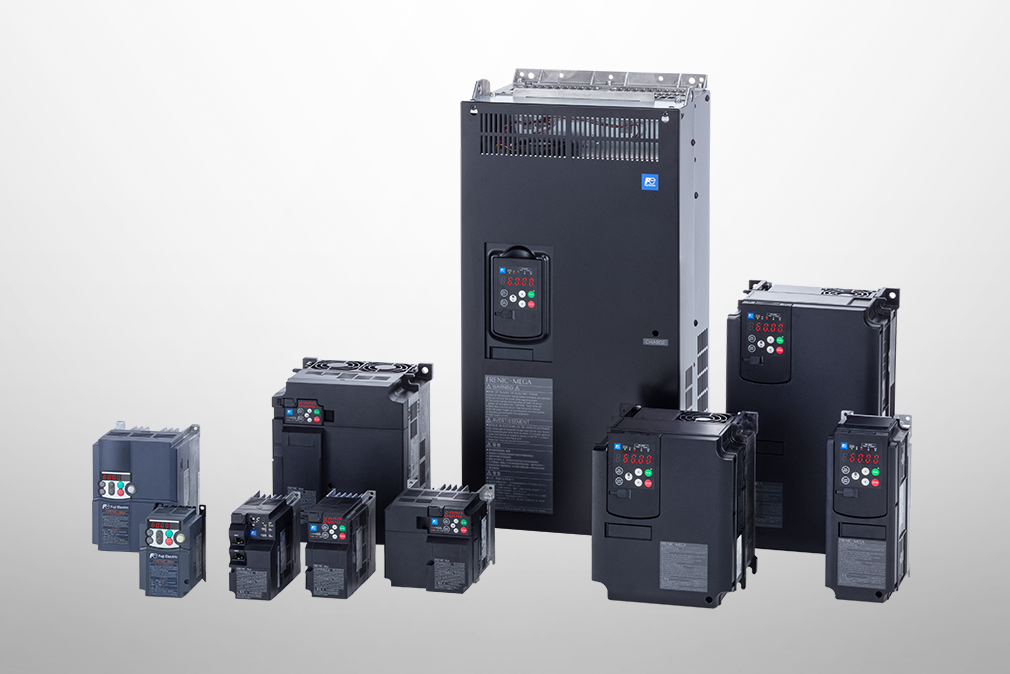
Fuji Electric Product Column
Inverters and converters

Inverters and converters
Understanding the basics: Differences between inverters and converters
-
What is an inverter? The outline will change depending on whether we're talking about a device or circuit
-
Showing signs of energy conservation by changing the motor rotation speed using an inverter device!
-
What is a converter? It's possible to hook up an external converter device to an inverter!
-
Pay attention to the converter device dedicated to power regeneration that is used together with the inverter device.
What is an inverter?
The outline will change depending on whether we're talking about a device or circuit
The outline will change depending on whether we're talking about a device or circuit
In the narrow sense, the term "inverter" refers to a circuit (function) that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). However, in Japan, many people think of an inverter as a "device" that changes the voltage and frequency at will.
In a broad sense, an inverter inputs alternating current with a constant voltage or frequency (for example, AC100V/50Hz or 60Hz supplied from a household outlet) and then converts it into different voltage and frequency before its output. Hence, it is different from the narrow meaning of "conversion from DC to AC", which may give rise to confusion.
What is the reason for this discrepancy? In order to have a good understanding, let’s first start by looking at the internal structure of an inverter. An inverter is composed of the front part and the rear part. The front part, the “converter circuit” converts AC to DC while the rear part, the “inverter circuit” converts DC to AC.
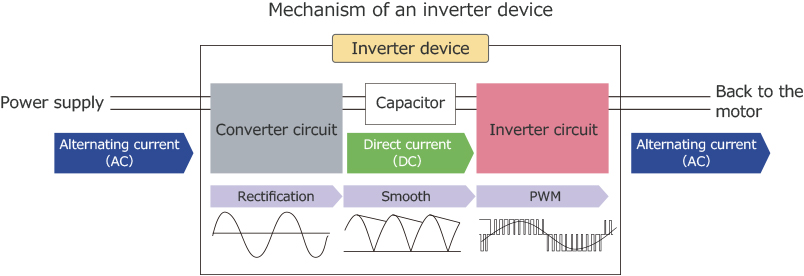
From a broad perspective, the converter circuit and inverter circuit are used as a set to perform AC to AC conversion. Whereas from a narrow perspective, inverters indicate the circuits and functions that are recognized as converting DC to AC. Keeping these differences in mind, we shall now move on to gain a better understanding of the inverter's mechanism.
Firstly, the converter circuit converts AC to DC. By combining diodes which only pass current in one direction, AC is rectified into a mountain-like shape and gradually changes its shape into a smooth direct current by charging and discharging capacitors.
Secondly, the inverter circuit outputs alternating current with varying voltage and frequency. Changing the on and off ratio using switching elements such as a power transistor will create a square-shaped pulse with different widths. The combination of these pulses leads to the output of a modified sine wave (AC). This method is called "Pulse Width Modulation" (PWM).
Showing signs of energy conservation by changing the motor rotation speed using an inverter device!
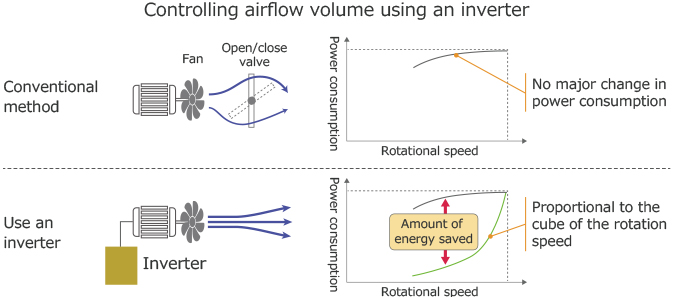
The main purpose of an inverter device is for it to continuously alter the rotation speed of a motor inside a machine by changing AC voltage or frequency. In addition, controlling the rotation speed using inverter devices reduces power consumption for industrial large-sized fans and pumps, resulting in energy conservation.
For example, say you want to reduce the airflow volume from a blower. Without an inverter device, you will need to adjust the airflow volume with a mechanical opening/closing valve. However, since the motor is rotating based on the power supply frequency, the amount of airflow generated from the motor is not being efficiently reused. This results in a waste of energy.
Instead, by using an inverter device, you can reduce the motor’s rotation speed directly, resulting in energy conservation since it is no longer necessary to block the wind mechanically. Keeping this in mind, generally speaking, power consumption from fans and pumps are proportional to the cube of the motor rotation speed, so by reducing the motor speed using an inverter, you can expect to save a considerable amount of energy.
Inverter circuits are also used in devices that do not use motors such as IH (induction-heating) cookers and fluorescent lights to make delicate adjustments to heat generation and brightness.
Take IH cookers as an example. They contain a coil that helps with heating up the pot itself. The inverter circuit creates a high-frequency alternating current that is supplied to the coil. In the case of fluorescent lights, this high-frequency alternating current assists by accelerating the lighting speed, thus generating enough brightness with lower power consumption. It also helps with reducing the flicker.
What is a converter?
It's possible to hook up an external converter device to an inverter!
It's possible to hook up an external converter device to an inverter!
A converter circuit is used to convert alternating current to direct current. The direction and height of the wave changes periodically since alternating current is a sine wave. Diodes are used to rectify the direction of the alternating current into the same direction, and then the capacitor will charge and discharge electricity, converting it into a flat and smooth direct current. The word “converter” does not only mean “converter circuit” as used inside the inverter device, but also as a stand-alone case to point out the converter device itself.
Pay attention to the converter device dedicated to power regeneration that is used together with the inverter device.
A stand-alone converter device does not work independently. It needs to be externally attached to the inverter device and be used as a set with the inverter device when using regenerative energy.
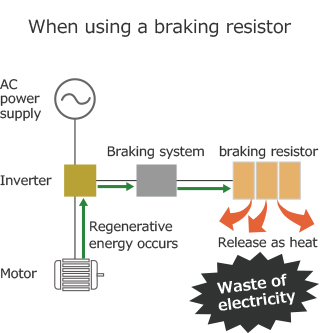
When a crane or elevator is being lowered or the carrier machine reduces its speed or stops, the motor turns with the momentum. In this situation, the motor is working as a generator and the electricity generated is called regenerative energy. There's risk that the device may be damaged if you leave the regenerative energy without taking any action as the inverter device will carry all the energy, thus increasing the voltage. To avoid this from happening, a resistor is connected to pass electricity and emit heat converted from energy.
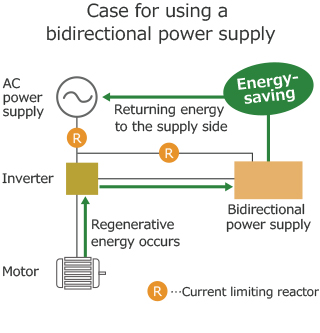
However, this is a waste of energy since it is just converting energy to heat without any purpose. This is where the regenerative converter device comes into play. By restoring the energy generated by this device to the power supply side, you can save energy. Regenerative energy can also be used for machines of similar types. For example, when braking a train, the regenerative energy created on the motor side can be sent to power another train.
Related products
Recommended

Understanding application, benefits, basic structure, case study, types, and Fuji Electric's inverters with this video.
December 27,2021

How and what does an inverter take control of? A brief explanation to grasp the basic structure.
January 20,2021

The fundamentals of inverters and their uses.
January 20,2021

