Sustainability
Efficient Use of Water Resources
In line with our Basic Environmental Protection Policy and Environmental Vision 2050, Fuji Electric aims to contribute to the achievement of a recycling-oriented society. To achieve this, we are promoting activities with the goal of realizing a circular economy throughout our entire supply chain.
Efficient Use of Water Resources
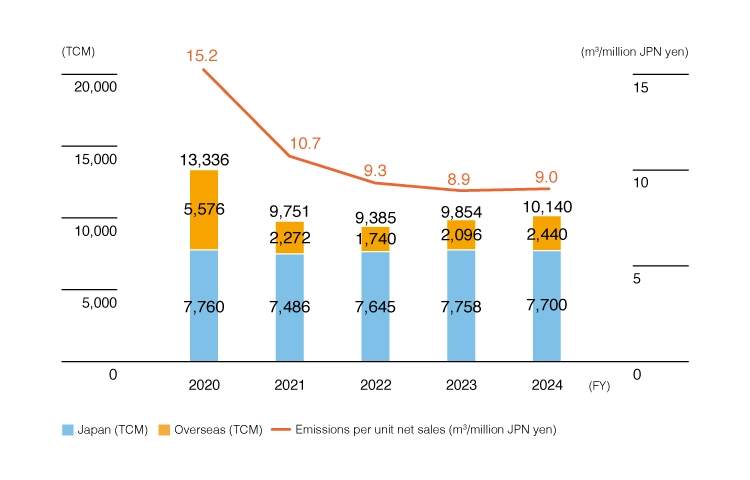
The issue of water resource depletion has become a global concern. Therefore, in addition to complying with wastewater standards, Fuji Electric has set targets for reducing water intake per unit of sales to promote the efficient use of water resources. In fiscal 2024, our company-wide water intake increased by 2.8% year-on-year, primarily due to increased semiconductor production at our Malaysia Factory. Nevertheless, our company-wide water intake per unit of sales remained at 900 m³ per 100 million yen.
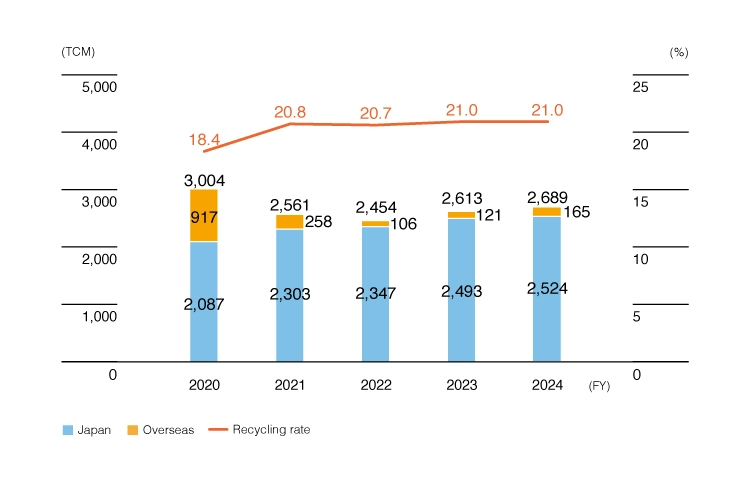
To utilize water resources more efficiently, we have also been advancing water recycling efforts. In order to improve our recycling rate, we installed additional recycled water production facilities at Matsumoto Factory, which began operations in December 2023. However, due to increased production at our Malaysia Factory, the water recycling rate for fiscal 2024 remained at 21.0%, the same as the previous year.
-
Note
-
We calculate “water usage volume” and “recycling rate” using the following formulae:
Water usage volume = water intake volume + recycled water volume
Recycling rate = recycled water volume / water usage volume
-
Note
-
Japan — volume of tap water purchased + volume of industrial water purchased + volume of groundwater used (only groundwater * used in production activities)
Overseas — Industrial water
-
*
-
Volume of groundwater does not include groundwater used for soil cleanup, for agricultural purposes, or for melting snow.
Water Stress Risk Assessment
Fuji Electric has conducted an assessment using Aqueduct 4.0* to identify whether any of our production sites worldwide are exposed to water stress risks. As a result, certain sites in the Asian region have been identified as having high water stress risk; however, it has been confirmed that the water intake volume at these sites is relatively low.
-
*
-
Aqueduct: A map of global water risks published by the World Resources Institute (WRI).
Our Shenzhen Factory in China, which produces photoreceptors, was evaluated with an Aqueduct 4.0 score of 2 out of 5, indicating a low-risk area. However, the region does not have large rivers, and the stability of water supply is generally considered a challenge due to increased economic activity and population growth. In fact, from 2021 to 2022, a severe drought occurred as a result of the La Niña phenomenon.
Taking these conditions into consideration, our company has classified the Shenzhen Factory as a water risk watchlist site and has implemented the following measures:
-
1.
Installation of a water storage tank to minimize production impact during temporary water outages
-
2.
Introduction of facilities for recycling wastewater (achieving a recycling rate of 80%, surpassing the target of 70% agreed with Shenzhen city)
Through these efforts, we are working to strengthen the stable water supply system in the Shenzhen region throughout the year.
-
Note
-
Water usage: Volume of Water purchased + recycled
-
Note
-
Water risk ratio: Volume of water purchased (Shenzhen Factory) / Total Group water intake
Status of water intake management
At Fuji Electric, the majority of our production facilities are located in industrial parks, which are supplied with both industrial water and drinkable tap water; some of our facilities use groundwater, too. We provide annual reports on groundwater intake volumes to the relevant authorities, and make efforts to ensure we use local water resources in an appropriate manner. We use groundwater at 15 of our 19 facilities in Japan, and it accounts for 53.7% of our total water intake volume. In the past, intake of groundwater has resulted in land subsidence in Japan; today, however, the government has established standards to ensure that water intake volumes are managed appropriately. Accordingly, social issues caused by water intake are almost non-existent.
Only one of our 14 overseas facilities use groundwater, and it accounts for just 0.05% of our total overseas water intake volume. At Matsumoto, Yamanashi, Tsugaru, and Malaysia Factories, which use particularly large volumes of water in their front-end semiconductor processes, and at Shenzhen Factory we promote water recycling as a way to control and manage water intake volumes.
At other sites, too, we act swiftly in cases where ISO 14001 environmental impact assessments identify significant impacts due to water consumption. In addition to conserving water in our everyday activities, we also work to ensure the early detection and repair of water leaks, invest in water recycling systems, and install above-ground piping for visualization purposes.
Status of wastewater management
We strictly control wastewater at factories that use chemical substances. We have also established our own standards for wastewater management, which are stricter than those mandated legally. If an abnormality is detected in the wastewater treatment system, we have resident repair personnel in place to respond immediately. If we detect inadequate pH adjustment or similar problem, our drainage outlets are automatically shut down to prevent wastewater that does not meet official standards from being discharged externally. This substandard wastewater is kept in drainage reservoirs until remediation is completed.
By strictly managing wastewater in these ways, we strive to minimize the impact of our activities on the ecosystem.
Efforts to effectively utilize water at our production sites
Matsumoto Factory uses large amounts of water in its front-end semiconductor processes, so it is making efforts to recycle water as a way of reducing its environmental load. Thanks to new recycled water production facilities that commenced operation in December 2023, in fiscal 2024 the Factory increased its use of recycled water by 10.5% compared to fiscal 2022, and also improved its recycling rate by 0.6%. Going forward, we will continue to strengthen our water recycling and our water intake reduction activities.
Topics
Efficient use of water resources at Matsumoto factory
Efficient use of water resources at Matsumoto factory
Our Matsumoto Factory, where we make semiconductor wafers, uses large amounts of pure water in the wafer fabrication process and a lot of water for cooling production equipment. Therefore, it is important that we reduce water usage and utilize our water resources effectively.

Pure-water recycling initiatives:
Wastewater from the manufacturing process is sorted and relatively high-quality portions are recycled as raw water for pure water production.
To enhance recovery of wastewater from the washing process, we have successfully made bioactivated carbon filters with Microbacteriaceae, known for its treatment capability of organic substances, and thus improved the recovery rate. For wastewater containing fluorine, which is harmful to the environment, we have introduced a dedicated wastewater recovery system that uses a reverse osmosis membrane to concentrate wastewater and reduce its volume. Moreover, clean water that has passed through the membrane is reused as raw water for making pure water.
Reducing chemical use at hydrofluoric acid treatment facilities:
The water purification process requires regular regeneration of ion exchange resins, which produces a mixture of acidic and alkaline wastewater. At Fuji Electric, we previously neutralized this wastewater and, after terminal treatment, discharged it into the public sewage system. Wishing to reduce our use of chemicals, we devised and introduced a new wastewater recycling system that separates high-concentration alkaline solution from wastewater, and reuses this alkaline solution to make the necessary adjustments to pH levels for our hydrofluoric acid treatment equipment. This has enabled us to reduce the amount of chemicals used, as well as overall costs.
Building a new wastewater recycling system
In addition to our existing Integrated Water Management (IWM) wastewater recycling system, in fiscal 2023 we commenced operations of a new wastewater recycling system. This new system is capable of recycling twice the volume of wastewater of the existing system and, thanks to various improvements, the treated water is of a high enough quality that it can be used for air-conditioning. This has enabled us to support the increased production of Si products and SiC products. Going forward, we will continue to consider ways to make efficient use of water resources.
