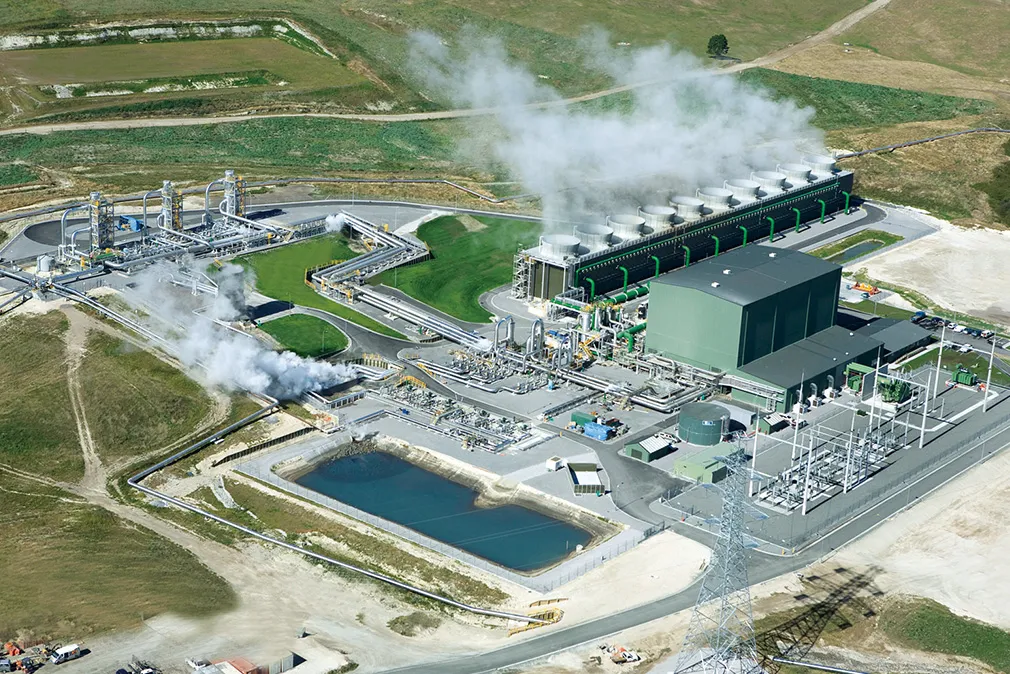
Fuel Cells

What is a fuel cell?
Generating Electricity Through Electrochemical Reactions
A Fundamental Concept
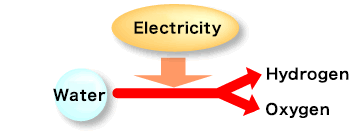
<Electrolysis of water>
Water electrolysis is a basic experiment commonly performed by students. When an electric current passes through water (H2O) using platinum or graphite electrodes, it splits into hydrogen and oxygen.
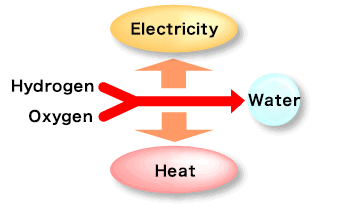
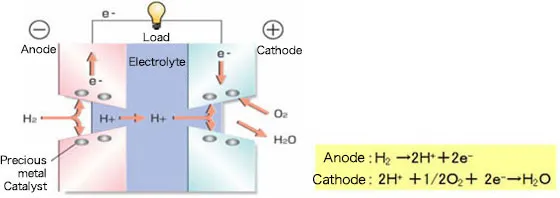
How a Fuel Cell Works: The Reverse of Water Electrolysis
A fuel cell operates by reversing the electrolysis process. Instead of splitting water, it combines hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. At the anode, hydrogen fuel undergoes a catalytic reaction, releasing hydrogen ions (H+) and electrons (e⁻). The electrolyte allows only hydrogen ions (H+) to pass through while blocking electrons. Electrons travel through an external circuit, generating electricity. At the cathode, oxygen (O2) reacts with hydrogen ions and electrons to form water (H2O) as a byproduct. This process makes fuel cells a clean and efficient energy source.