Home > About Fuji Electric > Research & Development > Technical Intelligence > Fuji Electric Journal > Fuji Electric Journal
FUJI ELECTRIC JOURNAL May/2004 (Vol.77-No.3)
 |
Water Processing Solutions |
Trends and Future Outlook for Water Processing Solutions
Shigeru Hatsumata, Tomoyasu Kida, Hiroshi Tada
Water-related problems are being discussed throughout the world. In Japan, higher quality and greater safety are demanded of water and sewage supply systems, and the processing of water is expected to bring about economic efficiency in the manufacturing industry. In the future, an autonomous decentralized metabolic system of water, based on a plan for a sustainable river basin area (holonic path), will probably be necessary. Fuji Electric intends to provide a water processing solution service capable of consulting on a vast array of issues including financial matters, systems and energy solutions that support optimization, and new processing technology such as sensors and membrane filtration that will help achieve higher quality and safer water.
Suggestion for an Integrated Water Environment Management System in a Watershed
Takashi Nakayama, Hitoshi Otsuki, Isao Somiya
Amid the growing worldwide concern for water problems, initiatives have been launched for the research and development of systems whose primary objective is to perform real-time monitoring and measurement and to provide information regarding the quality of water in an integrated basin environment. The "Study Group for an Integrated Water Environment Management System in a Watershed" was formed, research initiated, and at a subcommittee meeting held during the 3rd World Water Forum, water management plans were presented and discussed among the attendees. Also, in order to effectively utilize previously measured water quality data, an algorithm was presented for determining the changes in and correlation among riverwater quality data and interpolating sections where measurement data is missing.
Solution Service for Water Works
Takeo Ueno, Kazuyoshi Umezu, Hiroyuki Nakano
In the water works industry, there is a growing tendency to outsource work to the private sector. This paper describes the approach, history and tools used in the development of a broad-based waterworks solution service that includes operation management. The future outlook for such a service is also discussed. Aiming to enhance business performance and efficiency and to visually display and to quantify equipment status by means of digital computer technology, support tools have been applied to realize the PDCA cycle for a waterworks facility. This paper also presents solution menus for business consulting and service products.
Total Water Solution (Integrated Water Management) for Manufacturing Industries
Takashi Aoki, Tadashi Kunitani, Nobuyuki Shigematsu
Amid the prolonged deflationary economic conditions in Japan, in 2003, Fuji Electric Systems Co.,Ltd. and Nalco Inc. launched a solution service business, Integrated Water Management (IWM), which performs comprehensive water processing and management for the manufacturing industry. This IWM provides added value and economic benefits to customers as the result of water processing. The use of TRASAR technology, high concentrations and other means has achieved a 40 to 60 % reduction in chemical usage in the processing of water in a semiconductor plant's water-cooling system. Fuji Electric will remain committed to promoting this business in order to provide further added value to our customers.
Solution for Energy Management of Waterworks and Sewerage Facilities
Souichirou Yamamoto, Yoshinori Nagakura
In order to promote energy conservation and to improve the operational reliability of waterworks and sewerage facilities, the power supply for those facilities is required to be highly reliable. The majority of energy consumption in a waterworks and sewerage facility is used for such purposes as the transportation of water and air, and an uninterruptible power supply backup is required in order to ensure reliability of the power supply. This paper introduces the latest technological trends in PCS (power conditioning system) that use the elemental technologies of high-voltage VVVF (variable-voltage variable-frequency) and NAS (sodium-sulfur) batteries.
Study of a Photovoltaic System at the Ogouchi Reservoir
Souichirou Yamamoto, Masatoshi Ono
In response to the deteriorating quality of raw water in rivers and lakes, water utilities in metropolitan areas are working to ensure safe and good-tasting water by introducing high-grade water purification processing that uses ozone and activated carbon to improve and maintain the quality of the water supply. In 2002, the Tokyo Metropolitan Waterworks Department and Fuji Electric Systems completed a study of water quality improvement due to the clean energy obtained from photovoltaic generation at the Ogouchi Reservoir. This paper reports the results of that study, with a focus on photovoltaic generation.
A New Java-based Web Monitoring and Control System
Noboru Okuda, Masakazu Ikoma, Fukashi Koyama
In order to reduce the initial installation costs and to be able to deploy the latest technology, monitoring and control systems are increasingly using PCs and other general-purpose components. However, because general-purpose components are subject to frequent performance-enhancing upgrades and have a short lifecycle, there is need for some sort of improved solution. In response to this need, Fuji Electric has developed a Java-based monitoring and control system that is hardware and OS independent. Fuji calls its new system the Web- FAINS. This paper describes the development concept and features of the Web-FAINS.
An Automated Industrial Water Meter Reading System Using the DoPa Network
Takashi Ueno, Keiji Ishibashi, Katsutoshi Fujii
In recent years, a growing number of municipalities have been automating the task of reading water meters. At the same time, advances in wireless communications technology, such as cell phones, have been astonishing. Fuji Electric has developed an automated water meter reading system that uses the DoPa wireless network. This paper describes the development and actual example deliveries of this system for use in industrial waterworks.
Fuji Electric's Membrane Filtration System for Water Purifying Use
Kokan Kubota, Naruaki Kadokawa, Nobuyuki Motoyama
We investigated membrane filtration systems with the goal of introducing them to medium and large-scale water purification plants. Using surface water as raw water, a water purification plant in Mino, Okayama City was operated at a permeate flux of 1.5m3/(m2
 day) and
recovery rate of 92 %. The results of plant operation under these conditions
showed almost no increase in trans-membrane pressure difference,
and stable operation was achieved over a 6-month period. Using
membrane elements in which the hollow-fiber had been ruptured, we
examined the methods of fine-particle counting and membrane rupture
detection in order to assess the detection sensitivity.
day) and
recovery rate of 92 %. The results of plant operation under these conditions
showed almost no increase in trans-membrane pressure difference,
and stable operation was achieved over a 6-month period. Using
membrane elements in which the hollow-fiber had been ruptured, we
examined the methods of fine-particle counting and membrane rupture
detection in order to assess the detection sensitivity.
Automatic Trihalomethane Formation Potential Analyzer
Kouichirou Hosokawa Fumio Toyama Yoshiharu Tanaka
In order to reduce the amount of disinfection by-products such as trihalomethane (THM) that are formed in urban regions where organic pollutants are present in the raw water source, various solutions have been attempted at water purification plants, including injection of granular activated carbon and ozone processing. However, due to the lack of an instrument capable of automatically measuring the quantity of organic pollutants that contribute to the generation of disinfection byproducts, in cases where the quantity of organic pollutants changes dramatically within a short period of time, it has been difficult to achieve robust control of the appropriate amount of granular activated carbon or ozone to be injected. For this reason, as part of its series of equipment to help reduce disinfection by-products, Fuji Electric has developed a trihalomethane formation potential (THMFP) meter that automatically measures the THMFP.
Oil-on-Water Sensor
Naoki Kanekawa, Eiichi Masuzawa, Hideo Kanai
Oil spills are said to account for over 70 % of all river water pollution accidents. At a water purifying facility, such accidents have drastic consequences and result in the shutdown of the feedwater system and the like. Against this backdrop, Fuji Electric has developed an oil-onwater sensor for detecting oil film. The detection capability of this sensor is highly sensitive, relatively less susceptible to turbulent water and foreign objects, and is stable. For the commercialization of this sensor, the use of a unique new method known as polarization analysis has been proposed. Verification testing in simulated rivers and fields has yielded good results and plans are moving forward for delivery to a purification plant.
Sewerage Water Level Information System
Ken Sekine, Shinya Kobayashi
As measures to prevent urban flooding are coming under close scrutiny, local governments are focused on implementing urban flooding countermeasures in order to eliminate the possibility of floodwaters that could potentially have an enormous effect on urban functions. Under these conditions, the capability for early acquisition and provision of floodwater information is becoming increasingly important. As one type of flood prevention system, this paper introduces Fuji Electric's sewerage water level information system which measures the water level in a sewer pipe and transmits that data in real-time.
Treatment of Sludge from a Waterworks or Sewerage Facility Using a Filter Thickener with Siphon
Mikimasa Yamaguchi, Hironobu Kazui, Yoshio Tanaka
Sludge from a waterworks or sewerage treatment plant is usually thickened by a gravitational thickener and then processed to remove its water. It is important that the sludge be sufficiently thickened for such processing, but a sufficient thickness often cannot be achieved with a gravitational thickener, and this leads to decreased processing efficiency of subsequent-stage equipment and to deterioration of the return flow water quality. A siphon-type filter thickener operates so as to thicken sludge inside a filtration tank and discharges filtered liquid through a siphon attached to the top of a filter plate mounted in the tank, thereby separating the wastewater or sewerage sludge into highly concentrated thickened sludge and clear water. This paper introduces the thickening performance, design flow and effectiveness of the siphon-type filter thickener.
Wastewater Treatment Process by Means of Ozonation
Yasuhiro Kato, Masashi Yamazaki, Soichiro Kimura
Ozonation is extremely effective in sterilization and decomposing organic substances even in applications involving the processing of sewerage and wastewater. This paper describes the ability of ozonation to remove pathogenic microbes such as cryptosporidium that are highly resistant to sterilization and endocrine-disrupting chemicals that are in the environment. If the objective is to inactivate microorganisms, stable processing can be achieved by controlling the CT value (= concentration of dissolved ozone
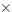 time) in an ozone contact tank. It
was verified that ozonation easily decomposes the typical endocrinedisrupting
chemicals of biphenol-A and 17
time) in an ozone contact tank. It
was verified that ozonation easily decomposes the typical endocrinedisrupting
chemicals of biphenol-A and 17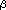 -estradiol.
-estradiol.
Application of Activated Sludge Simulation for Sewage Treatment Plant
Yuji Furuya, Takaaki Mizutani, Toshiki Fukushima
Fuji Electric has researched and developed an activated sludge bioreaction model for the purpose of application to the water quality measurement, operation management and control of an advanced sewerage treatment plant. This paper introduces an example application of the advanced sewerage treatment simulator over a 2-month period using the results of water quality analysis from an actual sewerage treatment plant. In addition to simulating the water treatment equipment that affects the quality of treated water, in order to evaluate the total operational and management costs and the amount of energy consumption at a water treatment facility, Fuji Electric will strive to improve its simulation technology to also take into consideration the operation of pump stations and sludge treatment facilities.

