Home > About Fuji Electric > CSR > Environmental Report > Topic 1/Reducing Environmental Impact through Our Products
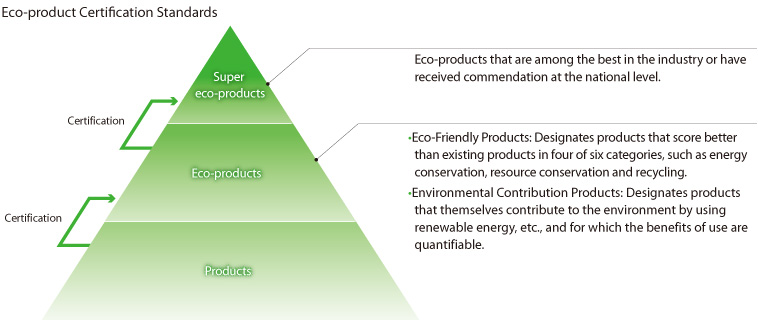
Creation of Eco-Products and Super Eco-Products
Fuji Electric evaluates the environmental contribution of products and consideration of the environment on a company-wide platform. Products meeting fixed standards for CO2 emissions volume reduction throughout society are designated “eco-products,” and of these, products which are tops in the industry in environmental performance and degree of environmental contribution or have otherwise received commendations from outside the company are designated “super eco-products.”
Our environmental medium-term plan for the three years through fi scal 2011 calls for expanding the ratio of eco-products in the overall Fuji Electric product lineup to 40%.
Target: 70% Net Sales Ratio for Eco-Products by 2020
Fuji Electric’s Environmental Vision 2020 sets the CO2 emissions reduction target for society overall at 2.4 million tons by 2020, and calls for the provision of energy-saving products and energy-creating products to help meet that goal. It also calls for sales of eco-products to make up 70% of total net sales by the same year.
In FY2009, we classified products that can contribute to CO2 emissions into four groups and devised quantitative CO2 reduction calculation methods for each. We were thus able to sum up total CO2 emissions reductions from products sold during FY2009 using these calculation methods. Our targets for FY2010 were “30% of total net sales comprised of eco-products” and “CO2 emissions volume reduction of 850,000 tons.” We exceeded the targets in both cases, coming in at 32.1% and 1.11 million tons reduction, respectively. For FY2011 we have set an eco-products sales ratio target of 40% and a CO2 emissions volume reduction target of 1 million tons, as we continue to work to create eco-products and increase the CO2 reduction effect.
Eco-Product Example 1: The “Eco Shopkeeper” Energy Monitoring Unit
Establishing Limits on Power Use and Supporting Total Energy Management at Retail Chain Stores
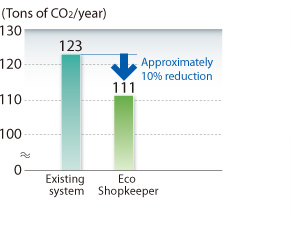
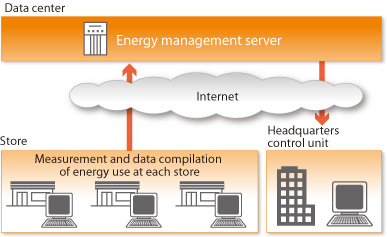
The revised Rational Energy Use Law requires chain stores and supermarkets to control the total energy usage of the chain, rather according to each individual store unit. This product not only measures power, but is also capable of setting limits on power use and sounding an alert prior to peak usage being reached, notifying the users of overuse of unneeded power. It can also be operated easily, even by people who don’t know a lot about electricity.
Use of this equipment provides an average energy conservation benefit of 5–10%, by analyzing the data gathered at each store and basing efficient usage strategies on that analysis. One application example for this equipment is its use in an office building that consumes 300 MWh annually. Improvements in some equipment as well as operational enhancement resulted in about 10% power use reduction. (Calculated based on a case at our company.)
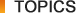
Eco-Product Example 2: Spot Air Conditioning System
Eliminating Heat Accumulation with Better Energy Conservation than Central Air
As data center server rooms trend toward greater capacities and integration, localized heat accumulation is becoming an issue.
This product, a spot air conditioning unit utilizing a high-efficiency coolant pump, eliminates heat accumulation problems. In FY2011, this unit has been achieving about 35% better energy efficiency than previously used central air conditioners.(Calculated based on a case at our company.)

 We Focused on Reducing Air Conveyance Power Usage in Developing an Energy-Saving Air Conditioning System
We Focused on Reducing Air Conveyance Power Usage in Developing an Energy-Saving Air Conditioning System
The volume of power used by IT equipment has been growing rapidly in recent years, and is projected to quintuple by 2025 in comparison with 2006 (METI). Therefore, we have been looking into ways to reduce the power used to drive air conditioners (especially that used in air conveyance), which makes up about half of the power used at Internet data centers. To that end we proposed a new air conditioning system by which a separate spot cooling unit (in-room unit) is placed within the server room.
In this system, the spot cooling unit is designed to hang from the server rack, which is unused server room space. The unit provides an energy-conserving way to eliminate local heat accumulation.

Atsushi Nakamura
Heat Application Technology Lab
Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
-
- Corporate Profile
- CSR
- Management Structure
- Social Report
- Environmental Report
- Topic 1/Reducing Environmental Impact through Our Products
- Topic 2/Reducing Environmental Impact at Our Production Bases
- Environmental Management
- Environmental Management Targets and Results
- Interplay between Business Activities and Environmental Impact
- Preventing Global Warming
- Recycling of Resources
- Management of Chemical Substances
- Preservation of Biodiversity
- Reducing Environmental Impact through Fuji Electric Products
- Together with Local Communities
- Research & Development


