Phát triển bền vững
Sử dụng hiệu quả tài nguyên nước
Phù hợp với Chính sách Bảo vệ Môi trường Cơ bản và Tầm nhìn Môi trường 2050, Fuji Electric đặt mục tiêu góp phần xây dựng một xã hội hướng đến tái chế. Để đạt được điều này, chúng tôi đang thúc đẩy các hoạt động hướng đến mục tiêu hiện thực hóa nền kinh tế tuần hoàn trong toàn bộ chuỗi cung ứng.
Sử dụng hiệu quả tài nguyên nước
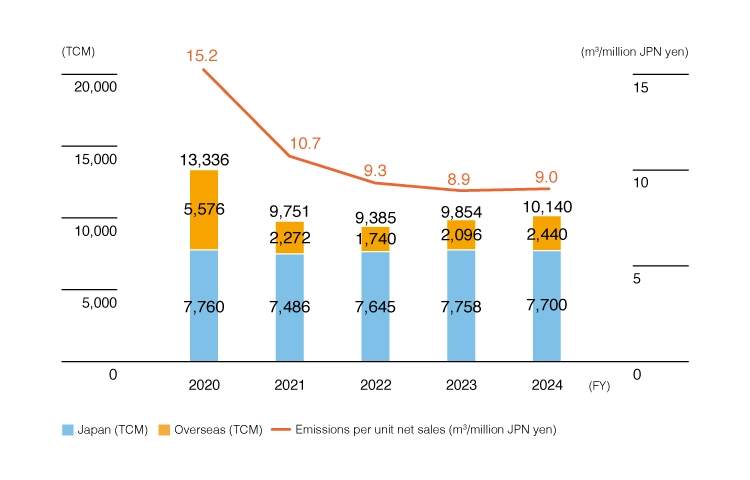
Vấn đề cạn kiệt tài nguyên nước đã trở thành mối quan ngại toàn cầu. Do đó, bên cạnh việc tuân thủ các tiêu chuẩn về nước thải, Fuji Electric đã đặt ra mục tiêu giảm lượng nước tiêu thụ trên mỗi đơn vị sản phẩm bán ra nhằm thúc đẩy việc sử dụng hiệu quả tài nguyên nước. Trong năm tài chính 2024, lượng nước tiêu thụ trên toàn công ty đã tăng 2,8% so với cùng kỳ năm trước, chủ yếu nhờ vào việc tăng sản lượng bán dẫn tại Nhà máy Malaysia. Tuy nhiên, lượng nước tiêu thụ trên mỗi đơn vị sản phẩm bán ra vẫn duy trì ở mức 900 m³ trên 100 triệu yên.
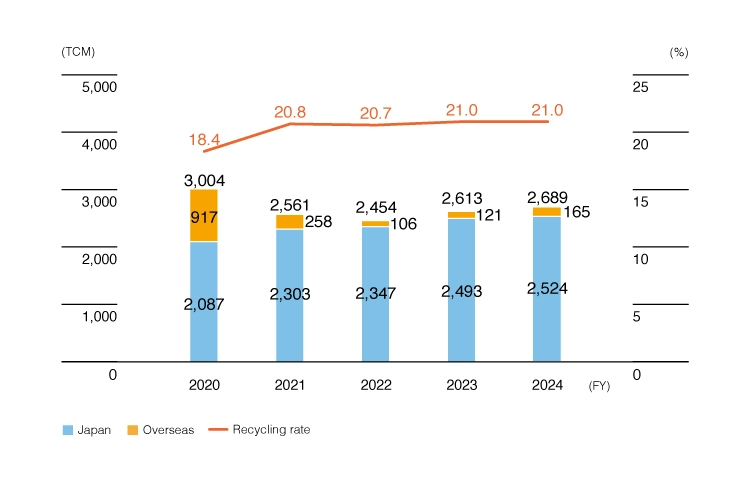
Để sử dụng tài nguyên nước hiệu quả hơn, chúng tôi cũng đã và đang đẩy mạnh các nỗ lực tái chế nước. Nhằm cải thiện tỷ lệ tái chế, chúng tôi đã lắp đặt thêm các cơ sở sản xuất nước tái chế tại Nhà máy Matsumoto, bắt đầu hoạt động vào tháng 12 năm 2023. Tuy nhiên, do sản lượng tại Nhà máy Malaysia tăng, tỷ lệ tái chế nước trong năm tài chính 2024 vẫn giữ nguyên ở mức 21,0%, tương đương với năm trước.
-
Ghi chú
-
Chúng tôi tính toán “lượng nước sử dụng” và “tỷ lệ tái chế” bằng các công thức sau:
Lượng nước sử dụng = lượng nước lấy vào + lượng nước tái chế
Tỷ lệ tái chế = khối lượng nước tái chế / khối lượng nước sử dụng
-
Ghi chú
-
Nhật Bản — khối lượng nước máy mua + khối lượng nước công nghiệp mua + khối lượng nước ngầm sử dụng (chỉ nước ngầm * sử dụng trong hoạt động sản xuất)
Nước ngoài — Nước công nghiệp
-
*
-
Thể tích nước ngầm không bao gồm nước ngầm được sử dụng để làm sạch đất, phục vụ mục đích nông nghiệp hoặc làm tan tuyết.
Đánh giá rủi ro căng thẳng về nước
Fuji Electric đã tiến hành đánh giá bằng Aqueduct 4.0* để xác định liệu bất kỳ nhà máy sản xuất nào của chúng tôi trên toàn thế giới có nguy cơ gặp rủi ro về thiếu nước hay không. Kết quả là, một số nhà máy ở khu vực Châu Á được xác định là có nguy cơ thiếu nước cao; tuy nhiên, lượng nước đầu vào tại các nhà máy này được xác nhận là tương đối thấp.
-
*
-
Đường ống dẫn nước: Bản đồ rủi ro về nước toàn cầu do Viện Tài nguyên Thế giới (WRI) công bố.
Nhà máy Thâm Quyến của chúng tôi tại Trung Quốc, nơi sản xuất tế bào cảm quang, được đánh giá với điểm Aqueduct 4.0 là 2/5, cho thấy khu vực có nguy cơ thấp. Tuy nhiên, khu vực này không có sông lớn, và sự ổn định của nguồn cung cấp nước thường được coi là một thách thức do hoạt động kinh tế gia tăng và dân số tăng. Trên thực tế, từ năm 2021 đến năm 2022, một đợt hạn hán nghiêm trọng đã xảy ra do hiện tượng La Niña.
Xét đến những điều kiện này, công ty chúng tôi đã xếp Nhà máy Thâm Quyến vào danh sách theo dõi rủi ro về nước và đã thực hiện các biện pháp sau:
-
1.
Lắp đặt bể chứa nước để giảm thiểu tác động đến sản xuất trong thời gian mất nước tạm thời
-
2.
Giới thiệu các cơ sở tái chế nước thải (đạt tỷ lệ tái chế 80%, vượt mục tiêu 70% đã thỏa thuận với thành phố Thâm Quyến)
Nhờ những nỗ lực này, chúng tôi đang nỗ lực tăng cường hệ thống cung cấp nước ổn định tại khu vực Thâm Quyến quanh năm.
-
Ghi chú
-
Lượng nước sử dụng: Lượng nước mua vào + tái chế
-
Ghi chú
-
Tỷ lệ rủi ro về nước: Khối lượng nước mua vào (Nhà máy Thâm Quyến) / Tổng lượng nước tiêu thụ của Tập đoàn
Tình hình quản lý lượng nước tiêu thụ
Tại Fuji Electric, phần lớn các cơ sở sản xuất của chúng tôi nằm trong các khu công nghiệp, được cung cấp cả nước công nghiệp và nước máy uống được; một số cơ sở của chúng tôi cũng sử dụng nước ngầm. Chúng tôi cung cấp báo cáo hàng năm về lượng nước ngầm cho các cơ quan chức năng và nỗ lực đảm bảo sử dụng hợp lý nguồn tài nguyên nước địa phương. Chúng tôi sử dụng nước ngầm tại 15 trong số 19 cơ sở của mình tại Nhật Bản, chiếm 53,7% tổng lượng nước ngầm. Trước đây, việc khai thác nước ngầm đã dẫn đến sụt lún đất ở Nhật Bản; tuy nhiên, hiện nay, chính phủ đã thiết lập các tiêu chuẩn để đảm bảo lượng nước ngầm được quản lý phù hợp. Nhờ đó, các vấn đề xã hội liên quan đến việc khai thác nước ngầm hầu như không còn tồn tại.
Chỉ có một trong 14 cơ sở ở nước ngoài của chúng tôi sử dụng nước ngầm, và nó chỉ chiếm 0,05% tổng lượng nước đầu vào của chúng tôi ở nước ngoài. Tại các nhà máy Matsumoto, Yamanashi, Tsugaru và Malaysia, nơi sử dụng lượng nước đặc biệt lớn trong các quy trình sản xuất bán dẫn đầu cuối, và tại Nhà máy Thâm Quyến, chúng tôi khuyến khích tái chế nước như một cách để kiểm soát và quản lý lượng nước đầu vào.
Tại các địa điểm khác, chúng tôi cũng hành động nhanh chóng trong trường hợp đánh giá tác động môi trường theo tiêu chuẩn ISO 14001 phát hiện những tác động đáng kể do tiêu thụ nước. Bên cạnh việc tiết kiệm nước trong các hoạt động hàng ngày, chúng tôi còn nỗ lực đảm bảo phát hiện sớm và sửa chữa rò rỉ nước, đầu tư vào hệ thống tái chế nước và lắp đặt đường ống nổi để quan sát trực quan.
Tình hình quản lý nước thải
Chúng tôi kiểm soát chặt chẽ nước thải tại các nhà máy sử dụng hóa chất. Chúng tôi cũng đã thiết lập các tiêu chuẩn riêng của mình về quản lý nước thải, nghiêm ngặt hơn so với các tiêu chuẩn bắt buộc theo luật định. Nếu phát hiện bất thường trong hệ thống xử lý nước thải, chúng tôi sẽ bố trí nhân viên sửa chữa tại chỗ để phản hồi ngay lập tức. Nếu phát hiện thấy việc điều chỉnh độ pH không đủ hoặc vấn đề tương tự, các cửa thoát nước của chúng tôi sẽ tự động đóng lại để ngăn nước thải không đạt tiêu chuẩn chính thức được xả ra bên ngoài. Nước thải không đạt tiêu chuẩn này được giữ trong các hồ chứa nước thải cho đến khi hoàn tất quá trình khắc phục.
Bằng cách quản lý chặt chẽ nước thải theo những cách này, chúng tôi nỗ lực giảm thiểu tác động của các hoạt động của mình lên hệ sinh thái.
Nỗ lực sử dụng nước hiệu quả tại các địa điểm sản xuất của chúng tôi
Nhà máy Matsumoto sử dụng một lượng lớn nước trong các quy trình sản xuất bán dẫn đầu cuối, vì vậy chúng tôi đang nỗ lực tái chế nước để giảm thiểu gánh nặng môi trường. Nhờ các cơ sở sản xuất nước tái chế mới đi vào hoạt động từ tháng 12 năm 2023, trong năm tài chính 2024, Nhà máy đã tăng mức sử dụng nước tái chế thêm 10,5% so với năm tài chính 2022, đồng thời cải thiện tỷ lệ tái chế thêm 0,6%. Trong tương lai, chúng tôi sẽ tiếp tục tăng cường các hoạt động tái chế nước và giảm lượng nước tiêu thụ.
Chủ đề
Sử dụng hiệu quả tài nguyên nước tại nhà máy Matsumoto
Sử dụng hiệu quả tài nguyên nước tại nhà máy Matsumoto
Nhà máy Matsumoto của chúng tôi, nơi chúng tôi sản xuất wafer bán dẫn, sử dụng một lượng lớn nước tinh khiết trong quá trình chế tạo wafer và rất nhiều nước để làm mát thiết bị sản xuất. Do đó, điều quan trọng là chúng tôi phải giảm lượng nước sử dụng và sử dụng hiệu quả các nguồn nước của mình.
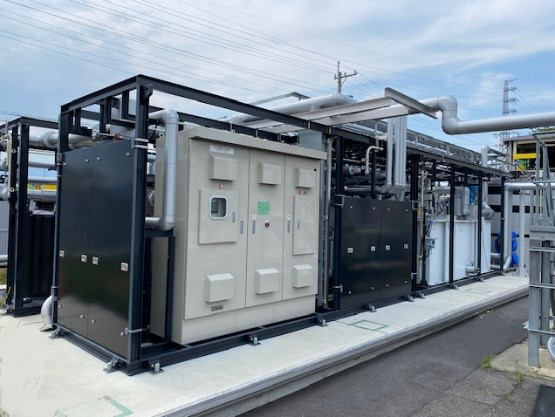

Các sáng kiến tái chế nước tinh khiết:
Nước thải từ quá trình sản xuất được phân loại và các phần chất lượng tương đối cao được tái chế thành nước thô để sản xuất nước tinh khiết.
Để tăng cường khả năng thu hồi nước thải từ quá trình rửa, chúng tôi đã chế tạo thành công bộ lọc than hoạt tính sinh học với Microbacteriaceae, được biết đến với khả năng xử lý các chất hữu cơ, và do đó cải thiện tỷ lệ thu hồi. Đối với nước thải có chứa flo, có hại cho môi trường, chúng tôi đã giới thiệu một hệ thống thu hồi nước thải chuyên dụng sử dụng màng thẩm thấu ngược để cô đặc nước thải và giảm thể tích của nó. Hơn nữa, nước sạch đã đi qua màng được tái sử dụng làm nước thô để tạo ra nước tinh khiết.
Giảm thiểu việc sử dụng hóa chất tại các cơ sở xử lý axit flohydric:
Quá trình lọc nước đòi hỏi phải tái sinh thường xuyên các loại nhựa trao đổi ion, tạo ra hỗn hợp nước thải có tính axit và kiềm. Tại Fuji Electric, trước đây chúng tôi đã trung hòa nước thải này và sau khi xử lý cuối cùng, xả vào hệ thống nước thải công cộng. Với mong muốn giảm lượng hóa chất sử dụng, chúng tôi đã thiết kế và giới thiệu một hệ thống tái chế nước thải mới, tách dung dịch kiềm có nồng độ cao khỏi nước thải và tái sử dụng dung dịch kiềm này để điều chỉnh mức pH cần thiết cho thiết bị xử lý axit hydrofluoric của chúng tôi. Điều này giúp chúng tôi giảm lượng hóa chất sử dụng cũng như tổng chi phí.
Xây dựng hệ thống tái chế nước thải mới
Bên cạnh hệ thống tái chế nước thải Quản lý Nước Tích hợp (IWM) hiện có, trong năm tài chính 2023, chúng tôi đã bắt đầu vận hành một hệ thống tái chế nước thải mới. Hệ thống mới này có khả năng tái chế gấp đôi lượng nước thải của hệ thống hiện có, và nhờ nhiều cải tiến, nước sau xử lý đạt chất lượng đủ cao để sử dụng cho điều hòa không khí. Điều này cho phép chúng tôi hỗ trợ việc tăng cường sản xuất các sản phẩm Si và SiC. Trong tương lai, chúng tôi sẽ tiếp tục nghiên cứu các phương pháp sử dụng hiệu quả tài nguyên nước.
