Operating principles
(ZSU, ZKJ)
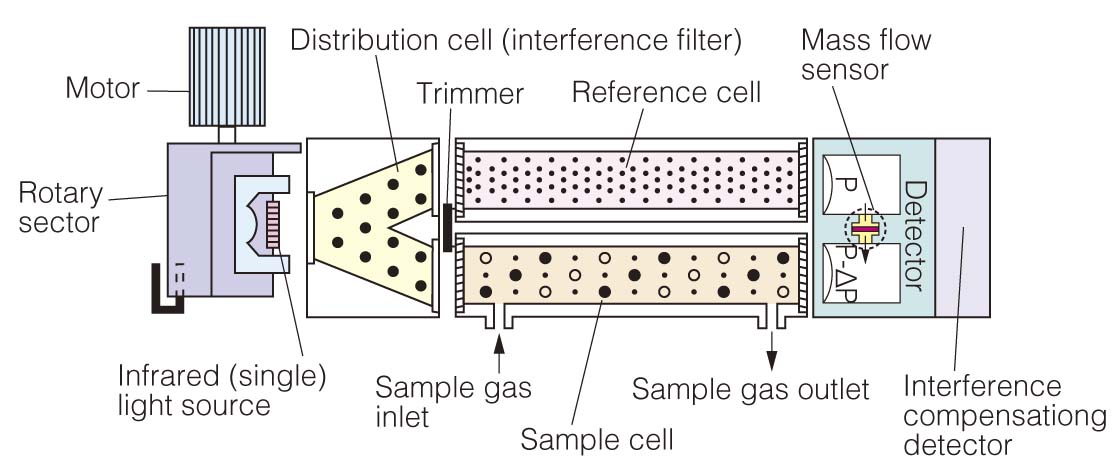
The amount of infrared rays absorbed by a sample cell is detected by the mass flow sensor.
(ZAJ)
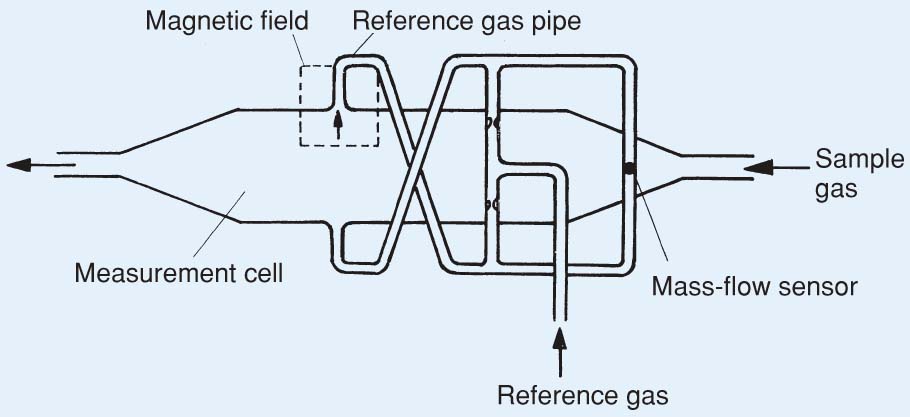
When the measured gas is placed in a magnetic field, oxygen molecules will be attracted. This gives rise to a pressure, which is detected by the mass flow sensor.
(ZSQ, ZSJ, ZPA, ZPB, ZPG, ZRE, ZRJ, ZSV)
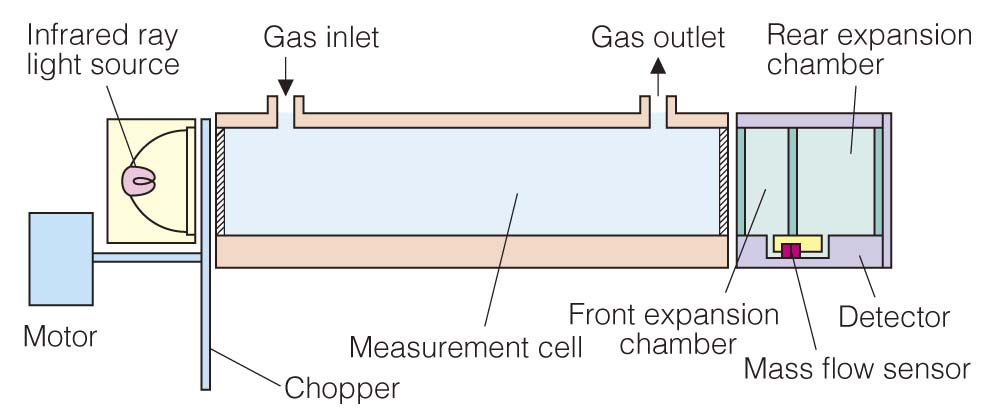
The amount of infrared rays absorbed by a sample cell is detected by the mass flow sensor.
(ZKG)
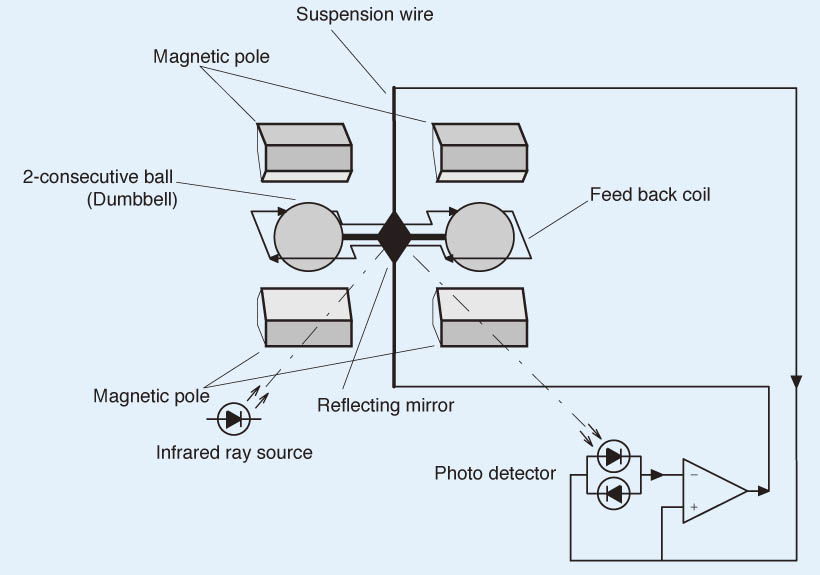
In the cell, two glass spheres filled with nitrogen gas are suspended with strong metal wire. When oxygen molecules having a large magnetic susceptibility flow there, the molecules are pulled toward the stronger magnetic field zone and the spheres are moved away from the zone. The resulting deviation of the spheres is detected with the light receiving element.
(ZFK)
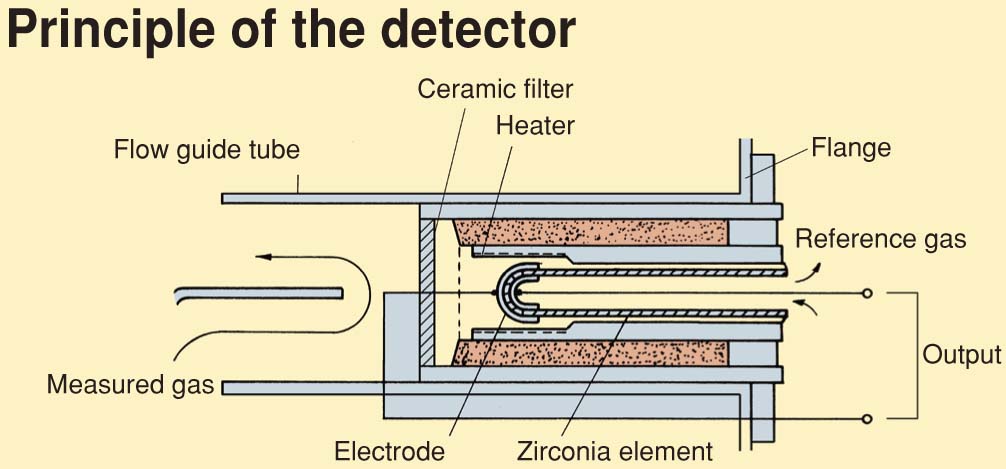
Detects Oxygen concentration by measuring the EMF (electromotive force) generated between the electrodes in the inside and the outsife of the Zirconia element
(ZAF)
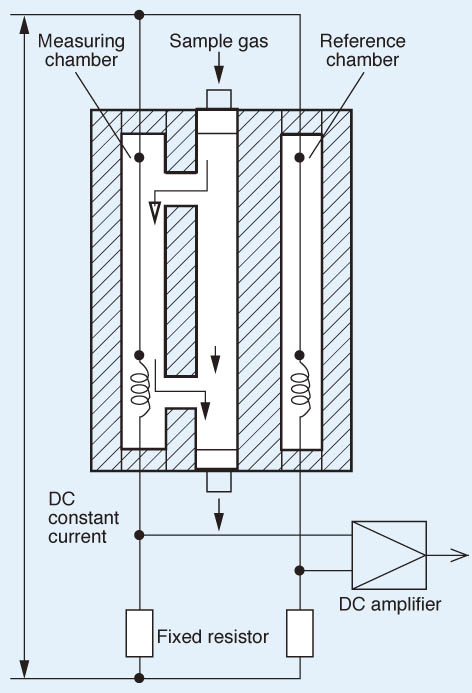
When there is a change in the concentration of the component under measurement, the thermal conductivity of sample gas will change to affect the temperature of the platinum wire in the measuring chamber. The resulting thermal change is taken out as a change in electric resistance, according to which the concentration of measured gas is calculated.





