One Step Ahead! Fuji Electric's Fundamental Technologies
We provide an overview of our latest fundamental technologies that enhance our product development capabilities.
Technology for Automation of Thin Sheet Metal Welding
Sensing and Robot Control Technology
Sensing and Robot Control Technology
Developed an automatic welding system to meet needs
for difficult welding work
for difficult welding work
The manufacturing industry is facing the problem of a shortage of technicians due to the Japan’s decreasing workforce caused by its aging population. To solve this problem, the need for automation of skilled work is increasing.
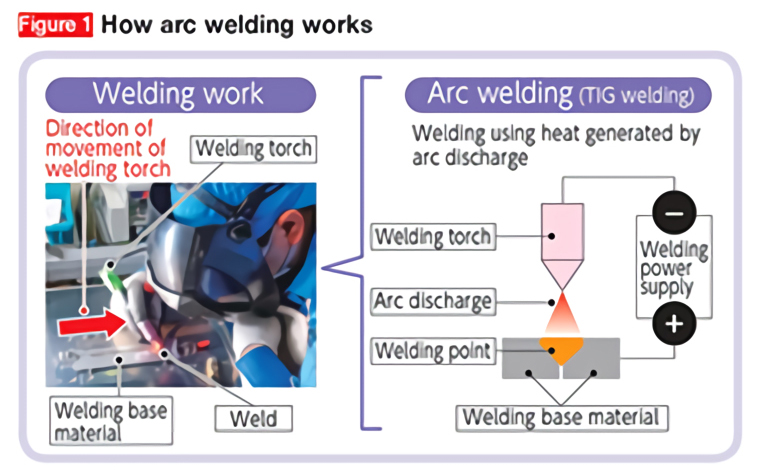
Since FY2016, we have been working on automation combined with robot control that makes use of sensing technology to digitize (visualize) the conditions related to welding quality. The subject here is arc welding of thin sheet metal. Arc welding involves running an electric current between the metal to be welded (base material) and an electrode (welding torch) to create an arc,* the heat of which is used to join the base materials of the metals ( Figure 1 ).
Thin metal sheet welding is performed in the manufacturing processes of various products. But there are difficulties when joining several pieces of sheet metal; for example, the thinness of the base material may cause a tendency to generate a slight gap or step (dimensional variation) between the base materials and a tendency toward deformation caused by the heat during welding.
Without adequate skills, this has led to poor welding and rework. For these reasons, we have combined sensing technology and robot control technology to develop an automatic welding system that allows stable, high-quality welding.
-
*
-
A type of discharge phenomenon
Achieved stable welding quality through sensing and robot control technology
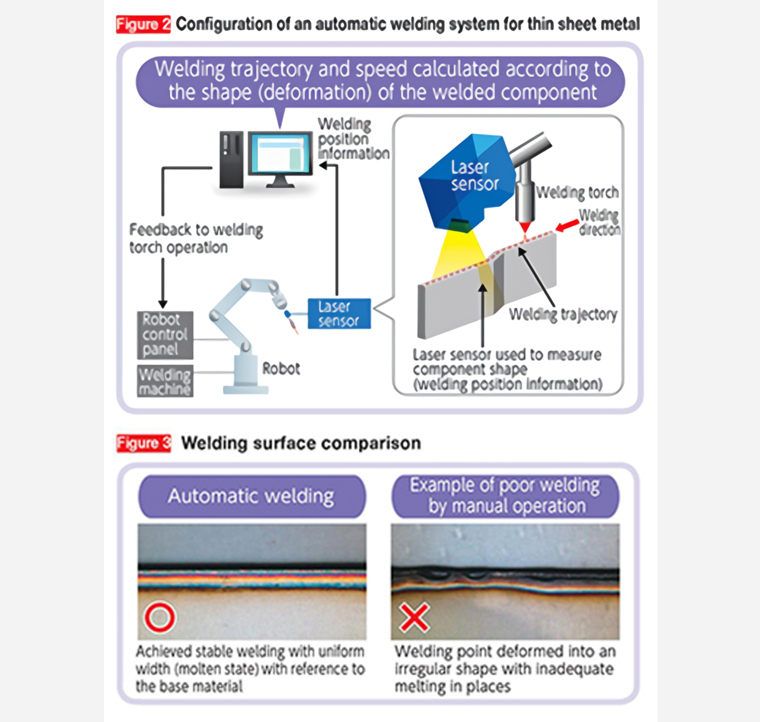
Thin sheet metal welding requires expertise to adjust the trajectory and speed of the welding torch while visually checking the shape (degree of deformation) of the joint surface and the molten state at the welding point. This automatic welding system uses a laser sensor to measure the shape of the joint surface to use the information as the basis for calculating the optimum trajectory and speed of the welding torch almost in real time. This is reflected in operation of the robot to reproduce the expertise ( Figure 2 ).
lso, in the prototyping process, we successfully improved the welding accuracy by looking at the shape data of sheet metal parts after welding to learn about the relationship between the welding speed and the molten state, then reflecting this information into the program. This has led to stable and high welding quality as compared with the conventional manual operation ( Figure 3 ).
In the future, we intend to first apply this system to a mass production line for component products to further reduce the welding time with the aim of in-house introduction by the end of FY2019.
Voices of developers

From now on, we plan to apply this technology to the welding of by manual operation large products for plants. In the future, we aim to contribute to improving productivity and quality by developing an advanced system that can independently determine and detect poor welding, analyze the causes, and solve the problem!
The article and the affiliations are at the time of coverage.
